Understanding Male and Female Connectors in Automotive Electrical Systems
One of the most basic but essential distinctions when working with automotive electrical connectors is between male and female connectors. Although the concept seems straightforward, confusion around identifying these parts is surprisingly common, especially when dealing with sealed or molded connectors in complex automotive harness systems.
This article outlines the characteristics of male and female connectors, accurately identifies them in automotive applications, and highlights common pitfalls to avoid during diagnosis and repair. What Are Male and Female Connectors?
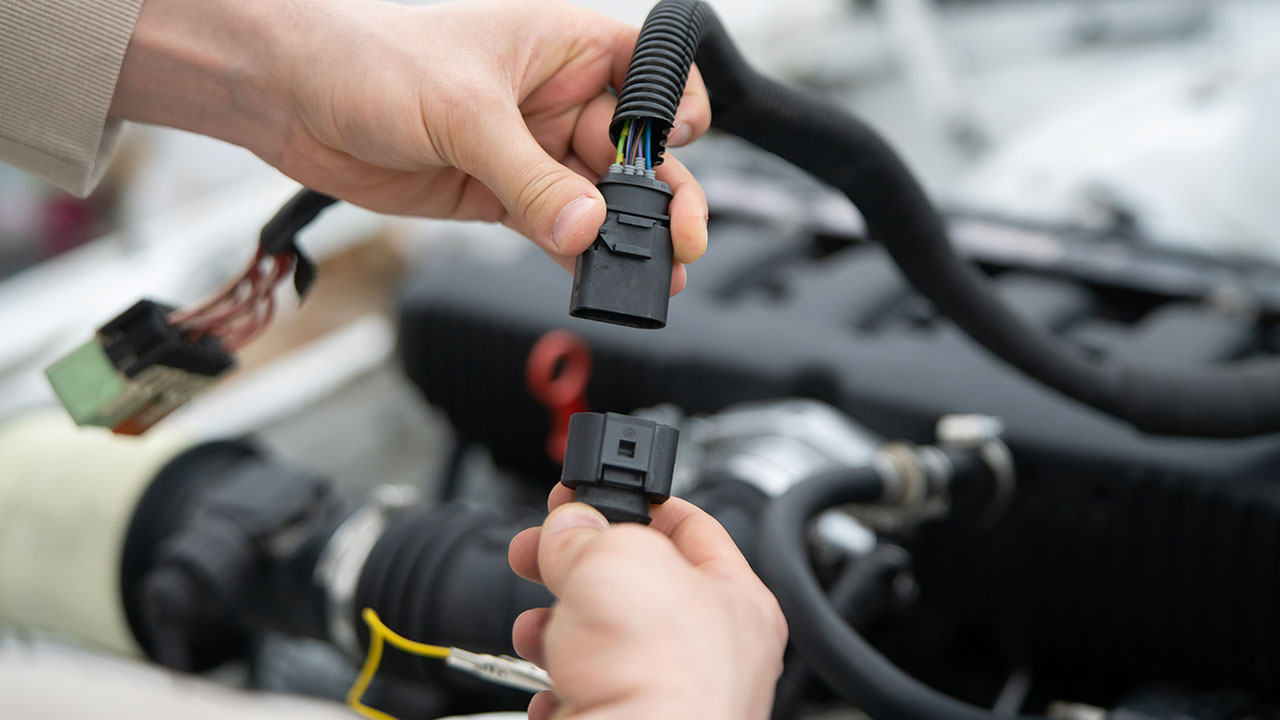

In electrical systems, the terms male and female describe the physical relationship between two mating components:
- Male connectors have protruding pins, blades, or tabs that insert into the corresponding part.
Female connectors contain sockets, tubes, or receptacles that receive the male terminals.
This “plug and socket” structure ensures a secure mechanical and electrical connection.

How to Identify Them in Automotive Applications
Unlike consumer electronics, automotive connectors are often molded, sealed, and built to withstand harsh environments. That means the external shape of the housing isn’t always a clear indicator of connector gender. Instead, identification relies on examining the internal contact terminals.
Key Tells:
- Male terminals: Typically metallic pins or blades that extend outward. Often found inside narrower cavities of the connector housing.
- Female terminals: These are tubular or slotted contacts recessed inside the housing. They are usually located inside larger openings or deeper sockets.
Tip: If unsure, open the connector or inspect the terminal side (not the wire side). The metal terminal, not the plastic housing, determines gender.
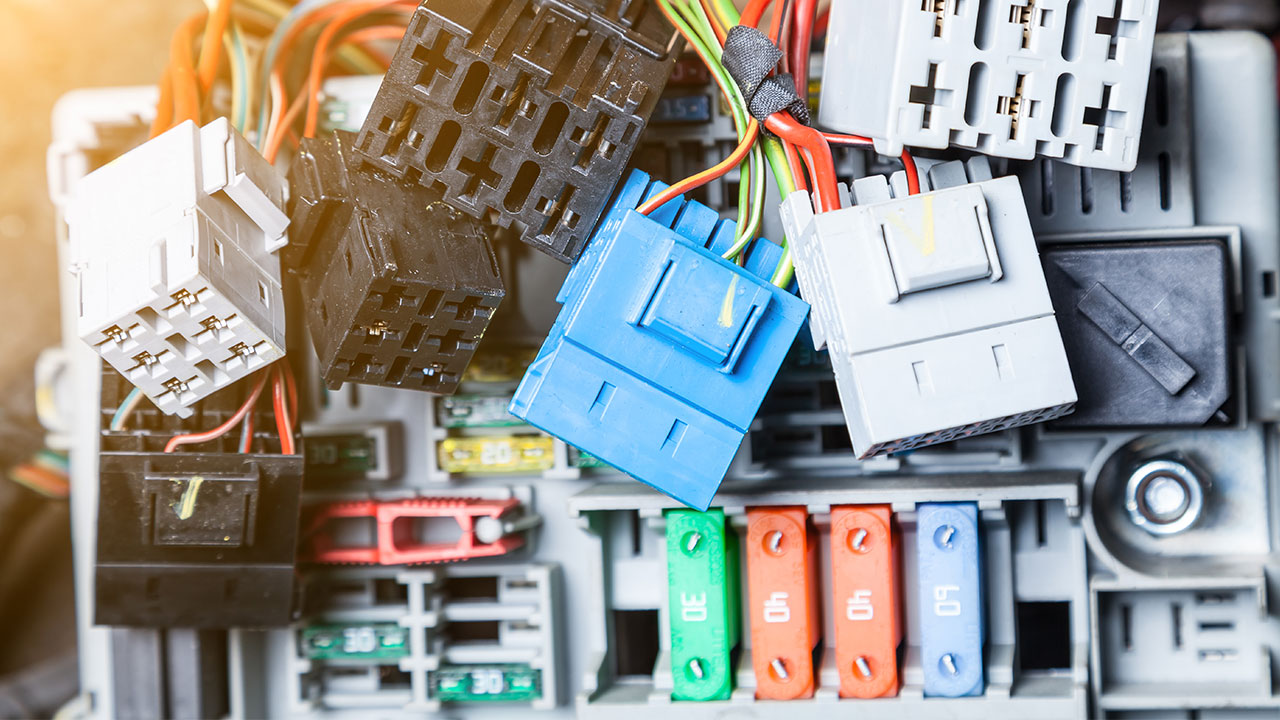
Where Are Male and Female Connectors Typically Found?
There’s no universal rule, but in most vehicle harnesses:
- Sensors and actuators (e.g., oxygen sensors, crankshaft sensors) often have male terminals on the sensor side and female terminals on the harness side.
- ECU connectors or main harness plugs tend to be female, while corresponding modules may have male headers.
- Light sockets and bulb plugs frequently contain female connectors, while the bulb or fixture has male pins.
This configuration helps reduce the exposure of live pins and improves weather-sealing performance, especially in exposed areas like under the hood or the body.
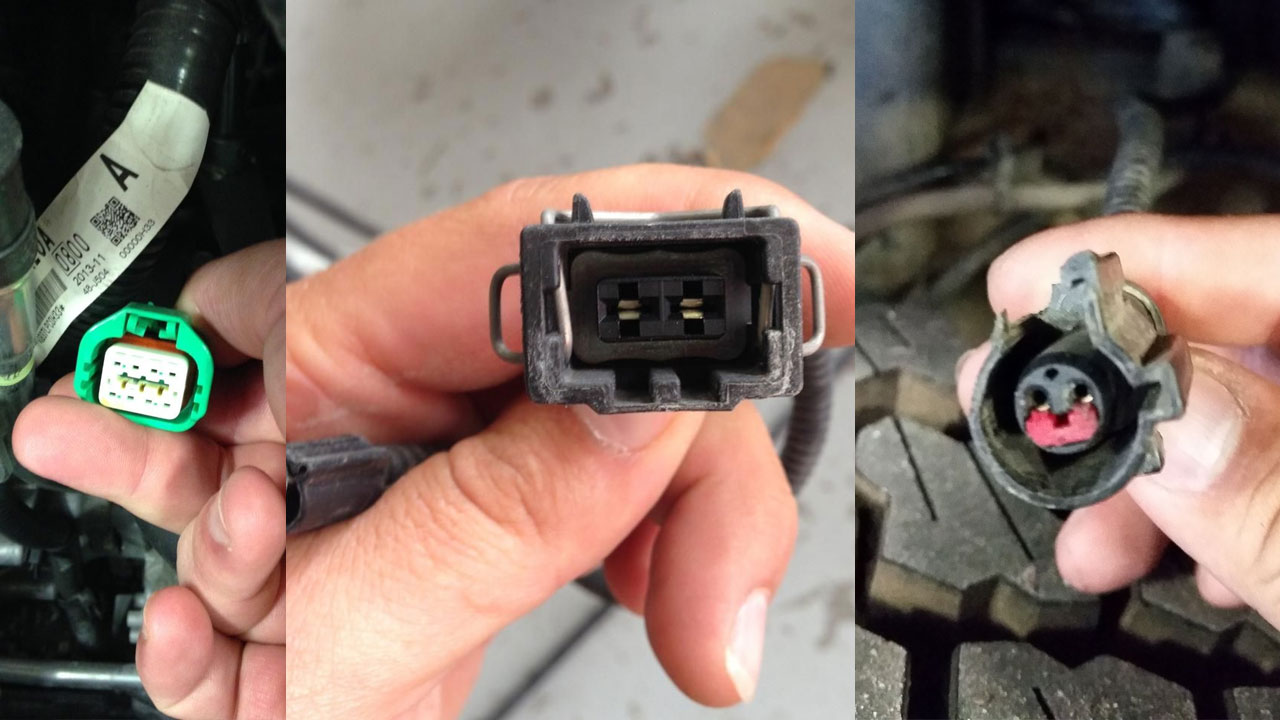
Common Issues with Connector Identification
Even experienced technicians can misidentify a connector's gender, especially when:
- The terminal is hidden within a sealed or weather-proof housing.
- The connector uses a flat blade terminal, which can appear ambiguous without closer inspection.
- Diagrams or part listings use unclear or reversed terminology.
Why It Matters:
- Ordering the wrong part: Mislabeling male/female can delay repairs and lead to compatibility issues.
- Poor terminal engagement: Incorrect matching of male/female pairs can cause intermittent signals or short circuits.
Increased wear: Forcing mismatched connectors can damage terminals or deform locking mechanisms.

Best Practices for Working with Connectors
- Physically verify the terminal type; don’t rely solely on visuals or online descriptions.
- Use a connector pinning diagram when available, especially with multi-pin connectors.
- When in doubt, compare both sides of the connector set; male and female are complementary, and identifying one confirms the other.
- Be cautious when reusing old connectors; terminal wear or corrosion can affect how gender is visually perceived.
Correctly identifying male and female connectors is more than terminology; it’s essential for accurate diagnostics, safe repairs, and proper part replacement in automotive electrical systems. Whether replacing a sensor pigtail, repairing a harness, or sourcing a connector, always confirm terminal type before proceeding.
Understanding the physical differences, typical applications, and pitfalls can significantly reduce errors and improve the quality of your repairs.

